Hbase is a distributed No SQL system built on top of HDFS(Hadoop distributed file system).
It is derived from Google's Bigtable and stores huge volume of structured or unstructured data over discrete columns instead of rows and provides consistent read and write access.This makes use this HBase feature for high-speed requirements .
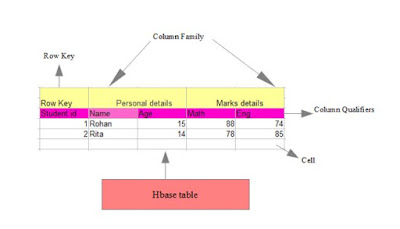
Data representation in Hbase Table:
An HBase table is divided into rows, column families, columns, and cells. Row keys are unique keys to identify a row, column families are groups of columns, columns are fields of the table, and the cell contains the actual value or the data.
Cell
Timestamp is a combination of date and time, used for versioning of data in hbase table.. Whenever data is stored, it is stored with its timestamp.
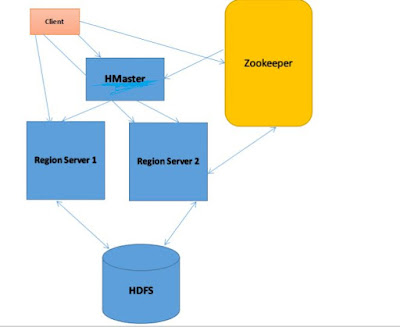
Hbase architecture:
There are 3 types of servers present in a master-slave type of HBase Architecture.
1. HBase HMaster
2. Region Server
3. Zookeeper.
Whenever a client sends a read/write request, HMaster receives the request and forwards it to the corresponding region servers. These servers serve data for reads and write purposes .Zookeeper, maintains live cluster state and coordinates with all components.
HMaster
HBase HMaster acts as a master server in Hbase architecture which assigns regions to region servers in the Hadoop cluster for load balancing and does DDL operations in cluster. There is only one HMaster exists in a cluster .In case of multiple master setup, there is only single active master at a time.
ZooKeeper:
Zookeeper is a centralized monitoring server which maintains configuration information and provides distributed synchronization.It Provides ephemeral nodes, which represent different region servers and tracks server failure and network partitions
Region Server :
Region server is responsible for handling and executing read, write, update, and delete requests from clients .
Each region server (slave) serves a set of regions which are comprised of Column families .
HBase tables are partitioned into multiple regions with every region storing multiple table’s rows. There are following components of a Region Server, which runs on an HDFS data node:
Block Cache – This is the read cache and stores frequently read data in memory . When the block cache becomes full, recently used data is evicted.
MemStore- This is the write cache .It stores new data which is not yet written to the disk. One MemStore exists per column family per region.
Write Ahead Log (WAL) -Write Ahead Log is a file on the distributed file system ithat stores new data that is not persisted to permanent storage.Moreover, we also use it for recovery in the case of failure.
HFile -It store the rows as sorted KeyValues on disk.

HBASE write:
1.When Client wants to write data , in turn first communicates with Regions server and then regions writes the data to the WAL (Write Ahead Log).
The edits are then appended at the end of the WAL file.
This WAL file is maintained in every Region Server and Region Server uses it to recover data which is not committed to the disk.
2. As soon as the data is written to the WAL , it is placed in the MemStore
where the data gets sorted and then, flushes into HFile. Memstore is used for storing data in a Distributed file system based on Row Key. Memstore are placed in Region server main memory and HFiles are written into HDFS. Only one MemStore exists per column family and updates are sorted per column family.
Hbase Read:
1.Client wants to read data from Regions ,the scanner first looks for the Row cell in Block cache. Here all the recently read key value pairs are stored.
2.if it fails then the data moves to memstore as Client can have direct access to Mem store, and it can request for data.
3. Client approaches HFiles to get the data. The data are fetched and retrieved by the Client.
Now you have got idea about basic architecture of hbase and how data flows through hbase insertion ,updation and read .
Please do follow and commenting if needed and we will be discussing hbase commands in next blog.





2 Comments
Very good
ReplyDeleteVery good
ReplyDeletePlease do not enter any spam link in the comment box